
Each AM station is assigned a specific carrier frequency that, by international agreement, is allowed to vary by In FM radio transmission, the frequency of the wave is modulated to carry this information, as illustrated in Figure 13.5.2, and the frequency of each station is allowed to use on each side of its carrier frequency. Fourier’s theorem implies that the modulated AM wave amounts to a superposition of waves covering some narrow frequency range. In AM radio transmission, the amplitude of the wave is modulated to mimic the vibrations of the sound being conveyed. In order to use an electromagnetic wave to transmit information, the amplitude, frequency, or phase of the wave is modulated, or varied in a controlled way that encodes the intended information into the wave.

ELF waves are able to penetrate sea water, which strongly absorbs electromagnetic waves of higher frequency, and therefore are useful for submarine communications.
There is no lowest frequency of radio waves, but ELF waves, or “extremely low frequency” are among the lowest frequencies commonly encountered, from to The accelerating charge in the ac currents of electrical power lines produce electromagnetic waves in this range.
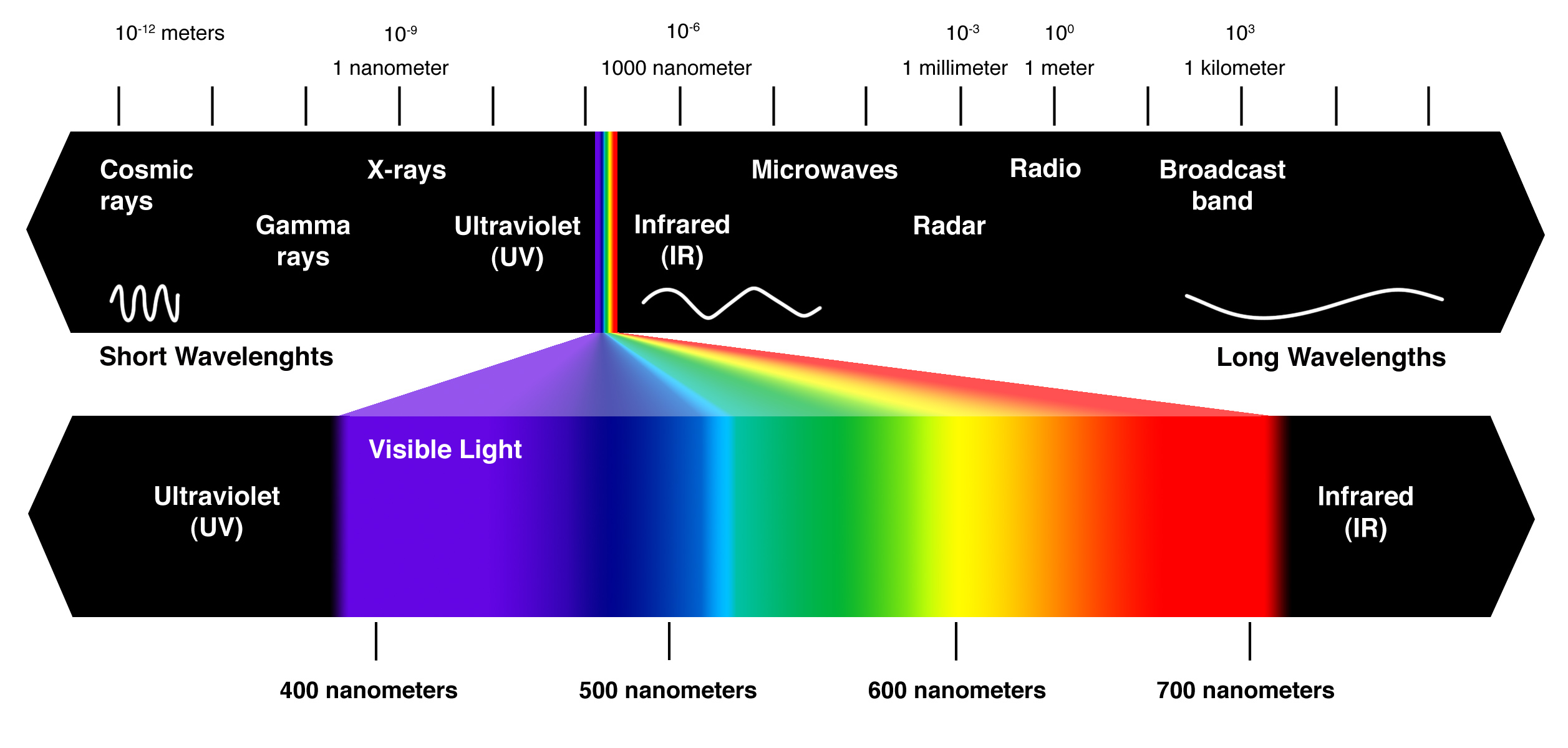
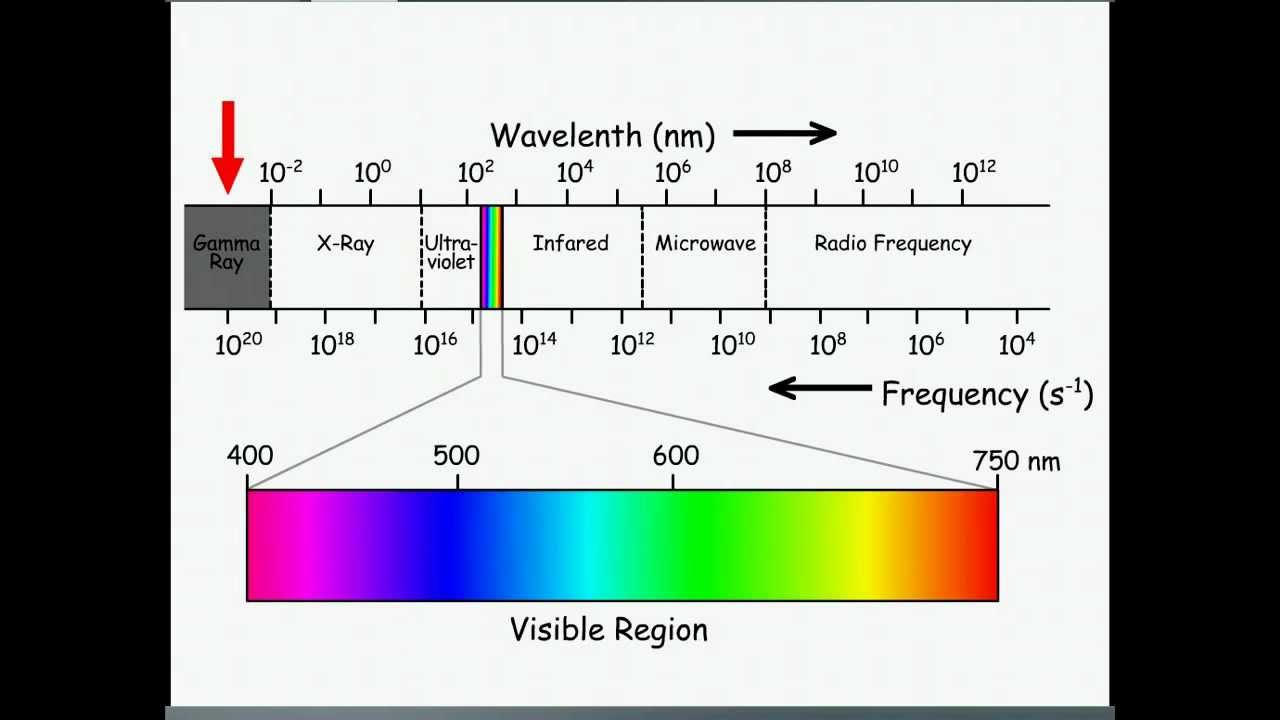
#ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM TV#
They cover a very broad wavelength range and are divided into many subranges, including microwaves, electromagnetic waves used for AM and FM radio, cellular telephones, and TV signals. Radio waves typically result from an alternating current in the wires of a broadcast antenna. The term radio waves refers to electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths greater than about Radio waves are commonly used for audio communications (i.e., for radios), but the term is used for electromagnetic waves in this range regardless of their application. A brief overview of the production and utilization of electromagnetic waves is found in Table 13.5.1.įigure 13.5.1 The electromagnetic spectrum, showing the major categories of electromagnetic waves. Their properties change smoothly from one frequency range to the next, with different applications in each range. The different categories of electromagnetic waves differ in their wavelength range, or equivalently, in their corresponding frequency ranges. We also summarize some of the main applications for each range. In this module, we discuss how electromagnetic waves are classified into categories such as radio, infrared, ultraviolet, and so on. Describe some of the many practical everyday applications of electromagnetic wavesĮlectromagnetic waves have a vast range of practical everyday applications that includes such diverse uses as communication by cell phone and radio broadcasting, WiFi, cooking, vision, medical imaging, and treating cancer.Describe how electromagnetic waves in different categories are produced.Explain how electromagnetic waves are divided into different ranges, depending on wavelength and corresponding frequency.By the end of this section, you will be able to:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
